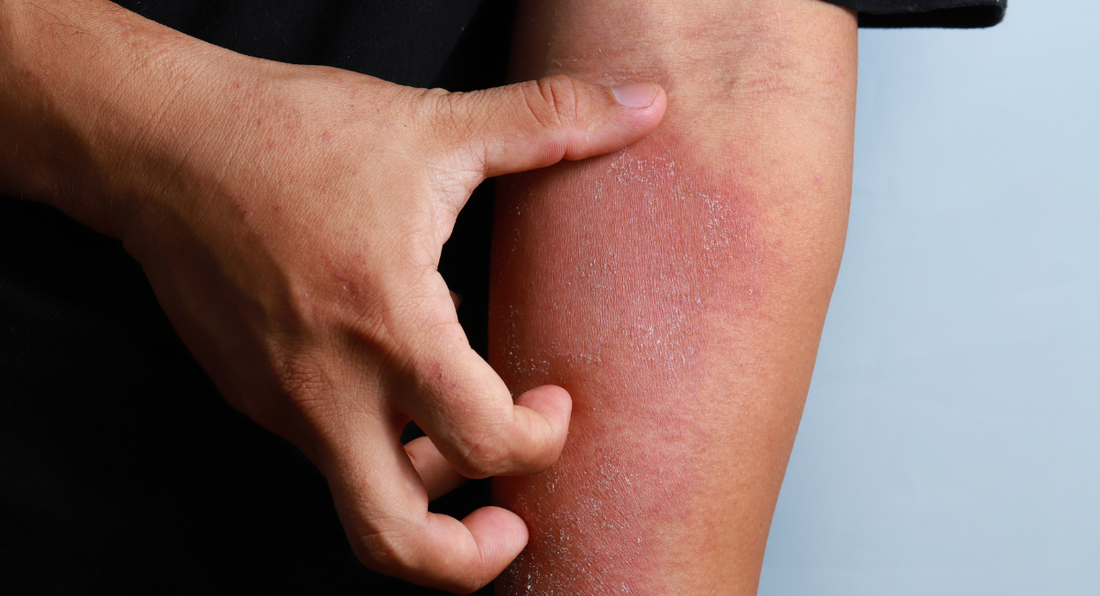
Eczema, a common skin condition, is often accompanied by an intense itch that can be incredibly difficult to ignore. However, giving in to the urge to scratch can lead to a host of complications. Understanding what happens when you scratch eczema is crucial for managing the condition and preventing further skin damage.
Damage to the Skin Barrier
When you scratch eczema-affected skin, it can lead to the breakdown of the skin barrier. This barrier is essential for protecting the deeper layers of skin from environmental irritants and allergens. Scratching can create small tears, making the skin more vulnerable.
Increased Risk of Infection
Broken skin is a gateway for bacteria, viruses, and fungi. People with eczema often have higher levels of Staphylococcus aureus on their skin, a bacterium that can cause infections. When the skin is broken from scratching, these microbes can enter and lead to infections, which may manifest as increased redness, warmth, swelling, or pus.
Worsening of Eczema Symptoms
Scratching can exacerbate eczema symptoms. It triggers a cycle known as the "itch-scratch cycle." The more you scratch, the itchier the skin becomes, leading to more scratching and further skin damage. This cycle can make eczema more severe and harder to treat.
Increased Sensitivity to Irritants and Allergens
Damaged skin is more susceptible to irritants and allergens like dust, pet dander, certain fabrics, and soaps. These substances can more easily penetrate the compromised skin barrier, potentially leading to more frequent and severe eczema flare-ups.
Lichenification and Permanent Skin Changes
Chronic scratching can lead to lichenification, where the skin becomes thickened and leathery. This change is a result of prolonged inflammation and can make the skin more prone to itching, perpetuating the cycle. In severe cases, these changes can become permanent.
Impact on Mental Health and Quality of Life
The constant itch and the need to scratch can be distressing and interfere with daily activities, including sleep. This can have a significant impact on mental health and overall quality of life.
Managing the Urge to Scratch
To prevent the negative consequences of scratching, it's important to manage eczema effectively:
- Moisturise Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated can reduce dryness and itchiness.
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: Understanding what exacerbates your eczema and avoiding these triggers can reduce flare-ups.
- Cool Compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth to itchy areas can provide relief.
- Wear Soft, Breathable Clothing: This can reduce skin irritation.
- Keep Nails Short and Clean: This minimises the damage if scratching does occur.
- Stress Management: Techniques like mindfulness and relaxation can help manage the psychological aspects of eczema.
Summary
Scratching eczema can lead to a range of complications, from infections to permanent skin changes. Understanding these risks is key to managing eczema effectively. If you're struggling to control the urge to scratch or your eczema symptoms, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for tailored advice and treatment. Remember, managing eczema is not just about treating the skin; it's also about breaking the itch-scratch cycle for long-term relief.